GALLUP NEWS SERVICE
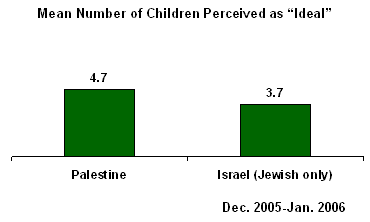
PRINCETON, NJ -- According to recent Gallup surveys conducted in Israel and Palestine as part of the Gallup World Poll, Palestinians living in the West Bank and Gaza Strip think the ideal number of children for a family to have is close to five per family, compared with close to four children preferred by Israeli Jews. That is not a large difference in a region where fertility could be a potent political tool.
These findings are based on nationally representative face-to-face surveys in Israel and the Palestinian territories of approximately 1,000 persons, aged 15 and older, conducted in December 2005 and January 2006.
Numbers Matter
The possibility that the once burgeoning Palestinian Arab population in Israel, the West Bank, and the Gaza Strip will eventually be the majority in that region has been widely accepted as a looming threat to Israel. It is one reason Prime Minister Ariel Sharon "disengaged" Israel from the Gaza Strip last year; because to annex Gaza -- with its estimated fertility rate of six births per Palestinian woman -- would only accelerate the religious shift within Israel. The concept of an inevitable Arab demographic threat has been influential in Israeli politics.
However, the assumption that Palestinians will eventually out-number the Jewish population in the region has come under recent criticism. A team of American and Israeli researchers (led by Bennett Zimmerman) reported in 2005 that the 1998-based prediction of a Palestinian majority by 2020 assumed the Palestinians' then 7.4 fertility rate (the average number of children born to women over their lifetimes) would be maintained, when, in fact, the Palestine Ministry of Health recorded a sharp decline by 2003 to about four births per woman. By contrast, the Jewish population in Israel has an average birth rate of 2.7 children per woman. This, combined with other factors such as net-immigration, lead the research team to believe Jews will continue to be in the majority.
The recent Gallup data is instructive because there is clearly an element of personal choice in having children, and thus Gallup finds strong evidence that people's preferred family size has a strong bearing on actual fertility rates. Gallup has been measuring Americans' notion of ideal number of children since 1936, and, except for the post-World War II "Baby Boom" period, the trend lines for preferred number of children and the U.S. fertility rate are quite parallel.
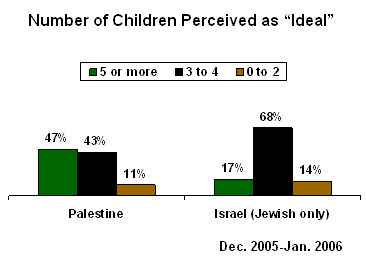
Most Palestinians and Jews Prefer Between Three and Six Children
Overall, close to half of Palestinians (47%) believe five or more children is the ideal, while 43% prefer three to four children and only 11% prefer less than three. Families of five or more are considered ideal by only 17% of Jews living in Israel, however 68% think three to four is ideal. Like the Palestinians, only a small number of Israeli Jews (14%) prefer small families of fewer than three children.
The net result is not an extraordinary difference in the mean number of children preferred by Palestinians (4.7) and Israeli Jews (3.7).
Arabs living in Israel are similar to Israeli-Jews on this measure. If combined with Palestinians living in the West Bank and Gaza Strip, the relatively small number of Israeli Arabs would only slightly reduce the mean number of children preferred by the Palestinians.
Having Children as a Religious or Political Decision
There are some major differences in preferences for number of children within each population.
Among Israeli Jews, the more conservative one's religion, the more children are preferred. Orthodox and religious Jews (representing 6% and 9% of the Gallup sample, respectively) think 5.3 children is, on average, the ideal for a family to have. Traditionalists, comprising 23% of the Israeli sample, think 3.9 children is the ideal, while secular Jews prefer only 3.1 children.
|
Israel: Preferred Number of Children According to Form of Judaism |
|||
|
Orthodox/Religious |
Traditionalist |
Secular |
|
|
% |
% |
% |
|
|
5 or more |
62 |
17 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 to 4 |
35 |
74 |
75 |
|
1 to 2 |
2 |
9 |
21 |
|
None |
1 |
0 |
* |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mean |
5.3 |
3.9 |
3.1 |
|
* Less than 0.5% |
|||
Among the Palestinians, those living in the Gaza Strip prefer more children than those in the West Bank, while the lowest preferred number is seen in East Jerusalem. This could be because residents of the Gaza Strip report higher rates of religiosity than those in the West Bank and East Jerusalem. Sixty-percent of those in Gaza tell Gallup they have attended a place of worship in the past seven days, compared with only 44% in the West Bank and East Jerusalem.
|
Palestinians: Preferred Number of Children According to Region |
|||
|
West Bank |
East Jerusalem |
Gaza Strip |
|
|
% |
% |
% |
|
|
5 or more |
43 |
28 |
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 to 4 |
46 |
56 |
35 |
|
1 to 2 |
10 |
14 |
10 |
|
None |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mean |
4.5 |
4.1 |
5.1 |
Palestinians with the least means to support large families -- those living in refugee camps -- are the most likely to favor having five or more children. Those living in villages show the least support for large families, while city residents fall in between.
|
Palestinians: Preferred Number of Children According to Place of Residence |
|||
|
City |
Village |
Refugee Camp |
|
|
% |
% |
% |
|
|
5or more |
47 |
38 |
68 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 to 4 |
43 |
48 |
29 |
|
1 to 2 |
10 |
14 |
2 |
|
None |
1 |
2 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mean |
4.8 |
4.2 |
5.6 |
Gallup finds no difference in preferred number of children by age in Israel, but does among Palestinians where those aged 50 and older prefer more than five children per family, compared with about 4.5 children preferred by those under 50.
|
Average Preferred Number of Children by Age Within Region |
||
|
Israel |
Palestine |
|
|
15 to 19 |
3.5 |
4.6 |
|
20 to 29 |
3.7 |
4.5 |
|
30 to 49 |
3.7 |
4.7 |
|
50 and older |
3.7 |
5.2 |
The answer to whether the Palestinians will eventually be the majority population in the region has enormous implications for the future of Israel, as well as a possible effect on the balance of power between Israel and the Palestinians as they pursue the peace process. However Gallup finds no evidence that attitudes about family size are related to one's view of the best way to resolve the Palestinian-Israeli conflict.
One of the questions in the more than hour long survey asked respondents to choose between "non-violent forms of resistance and negotiation" or "armed struggle and military solutions" as the better approach to achieving self-determination and security for their people.
In the Palestinian territories, those who believe in armed struggle are only slightly more likely than those who believe in peaceful solutions to prefer larger families -- but not significantly so. In Israel, the differences are also small, with those preferring non-violent solutions slightly more likely to favor large families.
|
Ideal Number of Children According to Preferred Approach to Achieving National Goals |
||
|
Palestine |
Israel |
|
|
Prefer non-violent solutions |
4.7 |
3.7 |
|
Prefer armed struggle |
4.8 |
3.6 |
Survey Methods
Palestinian results are based on face-to-face interviews with a nationally representative sample of 1,000 Palestinians, aged 15 and older, conducted Dec. 26, 2005 to Jan. 8, 2006. Respondents were interviewed in 52 sampling points throughout the West Bank (including East Jerusalem) and the Gaza Strip. Interviews were conducted in Arabic. Households were selected at random, and respondents within households were chosen at random according to Kish tables.
Israeli results are based on face-to-face interviews with a nationally representative sample of 1,002 Israelis, aged 15 and older, conducted Jan. 5-23, 2006. Respondents were interviewed in 120 sampling points throughout Israel. Interviews were conducted in Hebrew, Arabic, and Russian. Households were selected at random, and respondents within households were chosen at random according to Kish tables.
For results based on these samples, one can say with 95% confidence that the maximum error attributable to sampling and other random effects is ±3 percentage points. In addition to sampling error, question wording and practical difficulties in conducting surveys can introduce error or bias into the findings of public opinion polls.
|
Number of Children Perceived as "Ideal" for a Family to Have |
||||||
|
Palestine |
Israel |
|||||
|
|
Total |
Jewish |
Not Jewish |
|||
|
% |
% |
% |
% |
|||
|
7 or more |
14 |
4 |
4 |
4 |
||
|
5 to 6 |
33 |
13 |
13 |
10 |
||
|
3 to 4 |
43 |
68 |
68 |
69 |
||
|
1 to 2 |
10 |
15 |
14 |
17 |
||
|
None |
1 |
* |
* |
0 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
Mean |
4.7 |
3.7 |
3.7 |
3.7 |
||
|
* Less than 0.5% |
||||||